Unified Cloud-Native Data Protection for Your Hybrid Cloud
Protect your entire IT ecosystem — across on-premises, cloud, and virtual environments — with a single, modern platform from Commvault.

Overview Video
Commvault® Cloud Platform
Commvault Cloud powered by Metallic AI® is the first platform for true cloud cyber resilience, delivering the highest security, most intelligence, and fastest recovery.

How we do it
Comprehensive VM Protection for the Cloud Era
End-to-end protection
VMs – on-premises and in the cloud.
Snapshot & application backups
For optimal performance when restoring.
Unique storage flexibility
Ability to have on-prem copy for speedy recovery.
Anomaly detection & air-gapped copies
For ransomware protection.
Encryption of data in-flight and at-rest
Role-based, SSO, and SAML authentication controls.
Pre-configured and recommended plans
Built in standards and protocols.
CUSTOMER STORY
Nevada DOT Selects Commvault
See how the Nevada Department of Transportation simplifies backup operations and accelerates cloud transformation.

| Offered in 10-pack VMs | |
|---|---|
$102.49 per VM 10-pack / month | |
VMware | Yes |
Microsoft Hyper-V | Yes |
Microsoft Azure | Yes |
Amazon EC2 | Yes |
VMware Cloud on AWS | Yes |
Nutanix AHV | Yes |
OCI VM | Yes |
Volume discounts may apply for quantities over 50 VMs |
Offered in 10-pack VMs
$102.49 per VM 10-pack / month
VMware
Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft Azure
Amazon EC2
VMware Cloud on AWS
Nutanix AHV
OCI VM
- : Volume discounts may apply for quantities over 50 VMs
Our Reach
Supporting more than 100,000 companies
VM BACKUP FEATURES
Protection you need for cloud-native and on-premises workloads
Cloud-delivered simplicity for fast deployment, rapid value, and effortless management.

Exceptional flexibility
Commvault gives you the freedom to balance performance and cost across any storage environment.
Zero-Trust by design
Secure your hybrid cloud with an intuitive SaaS platform built for zero-trust protection and advanced cyber resilience.
Automated simplicity
Built-in standards and automated workflows keep your data protection always optimized and always on.
VM BACKUp INSIGHTS
Cloud-native data protection for your hybrid world.
Simplify VM backup with cloud-delivered protection—so you can focus on innovation, not infrastructure.
Exceptional flexibility
Freedom to optimize cost and performance across any environment—BYO, on-prem, or in the cloud.
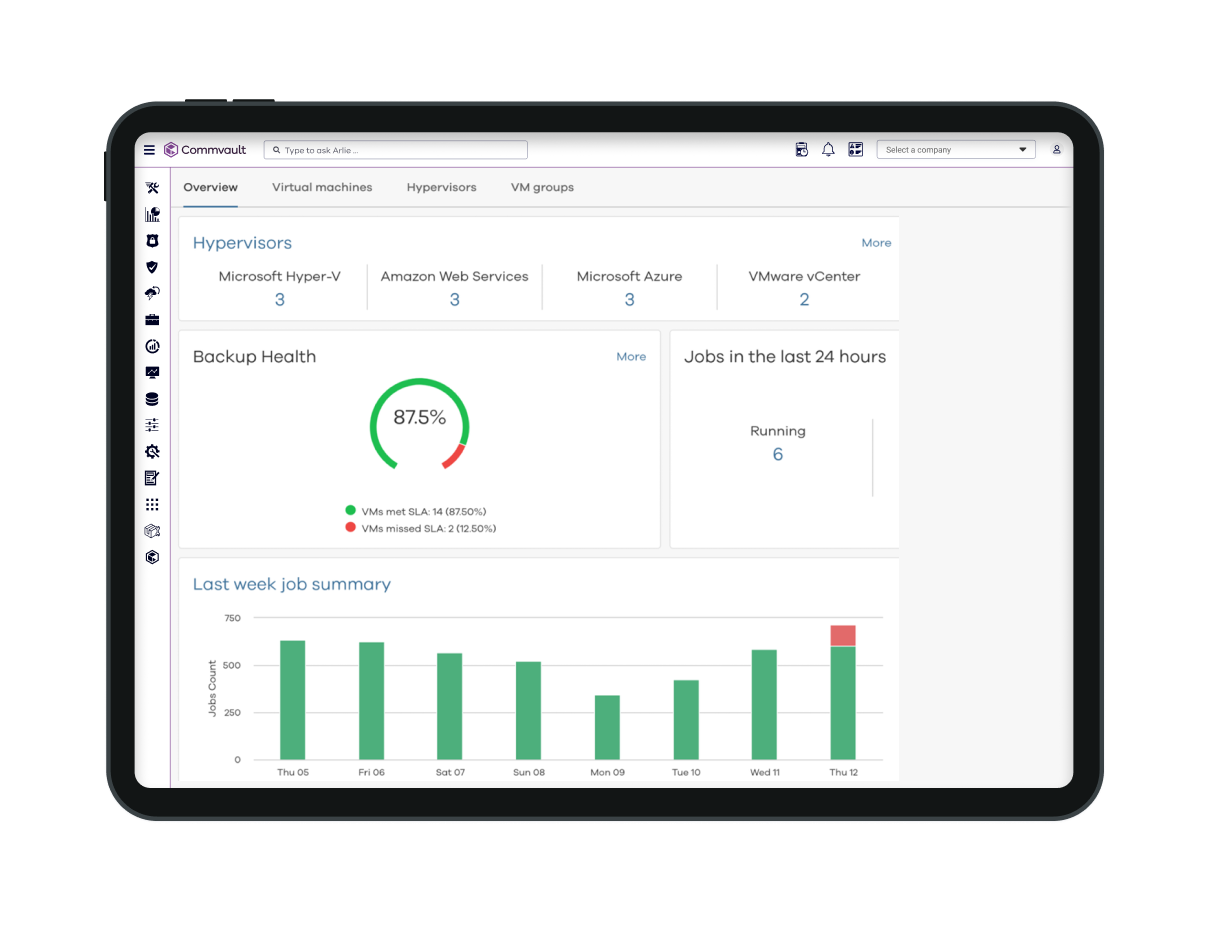
Meet compliance requirements with confidence.
End-to-end encryption, layered defenses, role-based access, and ransomware resilience—all in one platform.
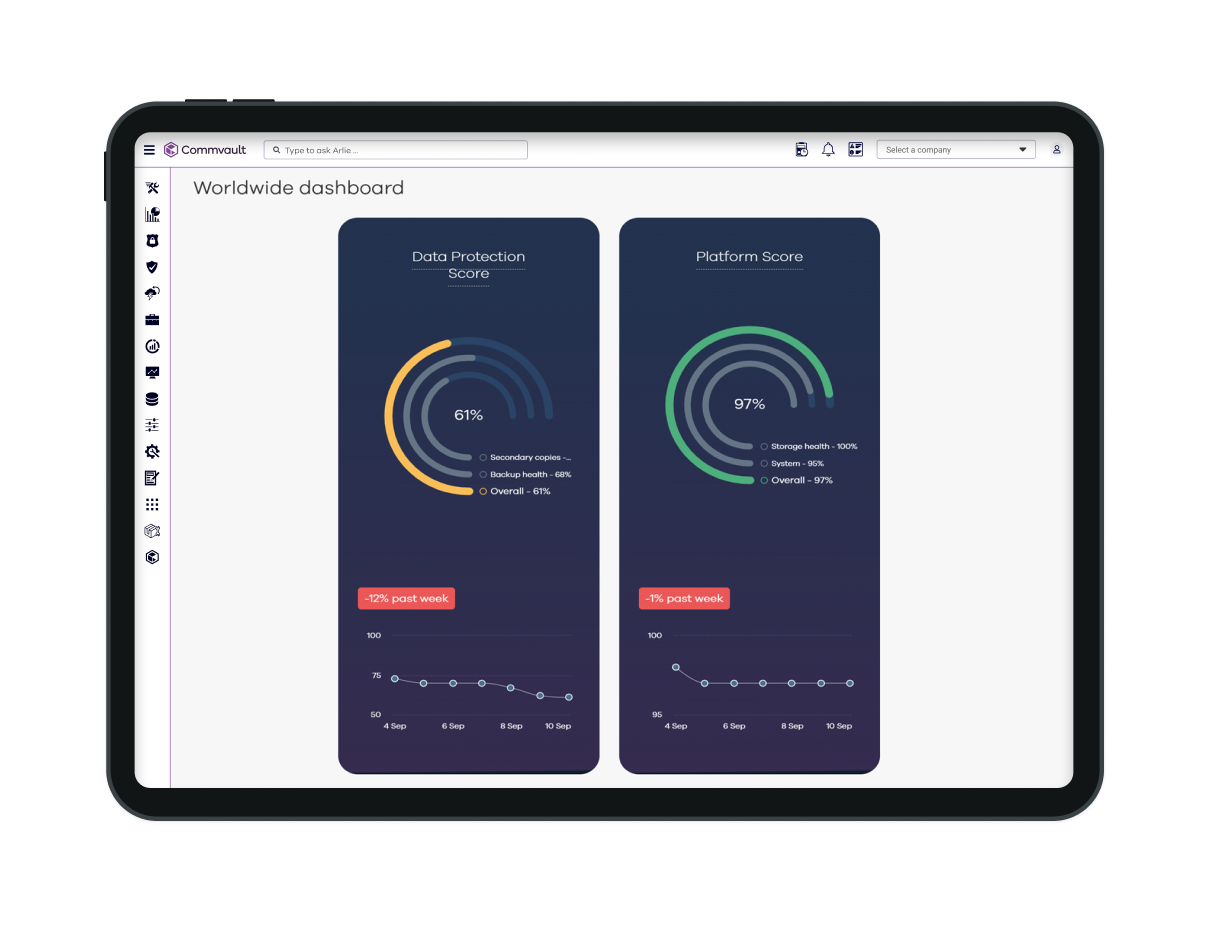
Hassle-free management
Pre-tuned standards and intelligent automation keep your data protection optimized.

Najm Protects Critical Data With Commvault

Commvault® Cloud for VMware

Commvault® Cloud Backup & Recovery for VMs
see it in action
Schedule a free demo
See how easily Commvault’s cyber resilience solutions can protect, defend, and deliver uninterrupted access to your data.